06
Feb
If you work with metal in Ontario, whether you’re a seasoned fabricator in Hamilton, a farmer repairing equipment in Perth County, or a DIY enthusiast building a custom barbecue in your Barrie garage—you know that cutting metal cleanly and efficiently is half the battle. From portable units to CNC systems, understanding various plasma cutter types helps you choose the right tool for your project. Enter the plasma cutter: a powerful machine that slices through steel, aluminum, and other metals with a focused jet of superheated plasma, delivering speed, precision, and cleaner cuts than traditional methods.
When you visit any Canadian retailer store like Princess Auto, Brafasco, or even browse online on Kijiji, and you’re met with a dizzying array of options. From compact “plug-in-your-garage” units to industrial behemoths, how do you choose? Making the wrong choice can mean wasted money, frustration, and project delays.
According to Workforce Planning Ontario’s 2026 projections, high-skill trades like welding and metal fabrication continue to face significant demand, with an estimated 7,100 job openings in the welding-related sector in Ontario alone over the next five years, highlighting the need for efficient tools like plasma cutters.
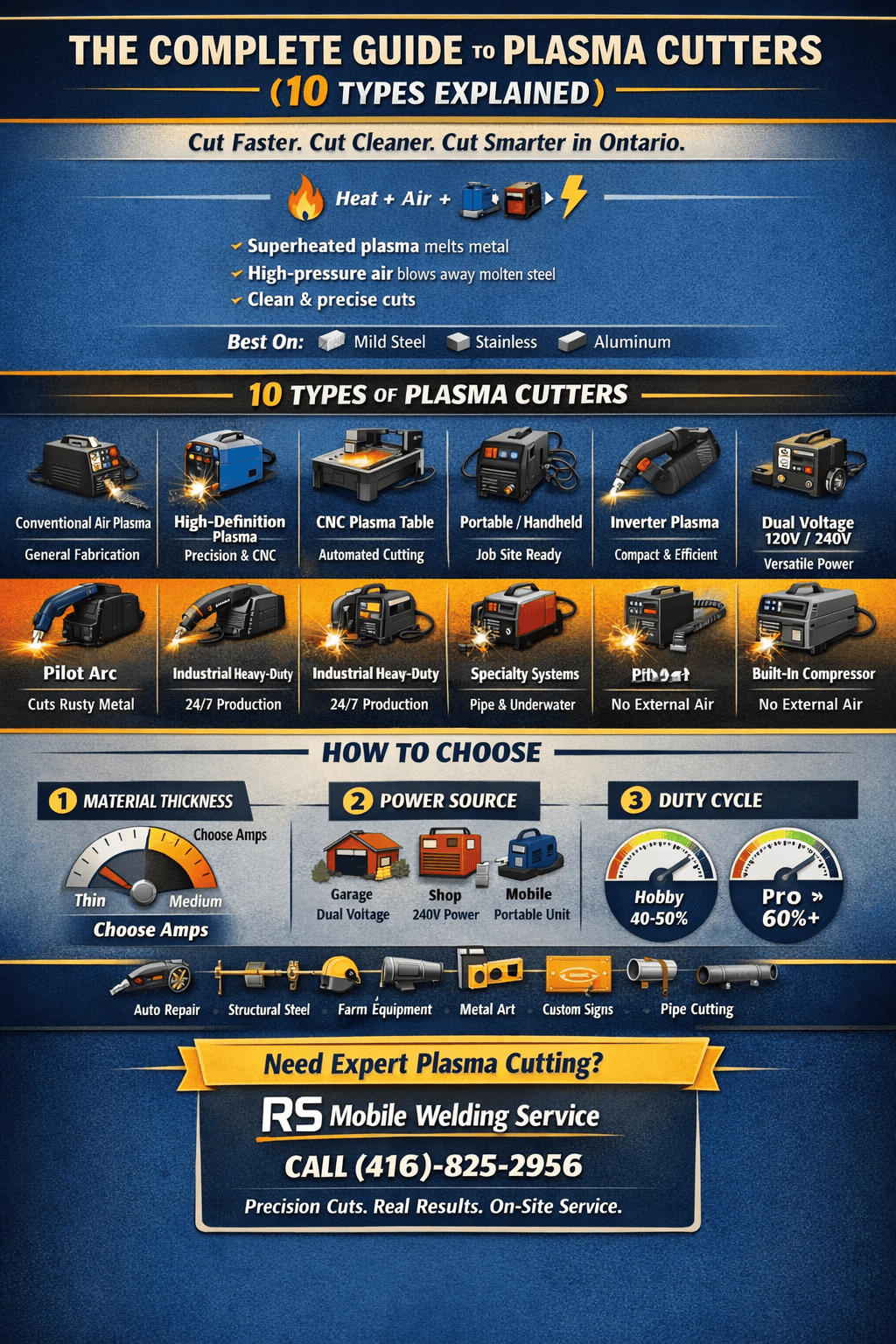
In this guide, we’ll break down the 10 primary types of plasma cutters, and give you a clear, actionable framework to select the perfect machine for your projects, shop, and budget. Let’s power up and dive in.
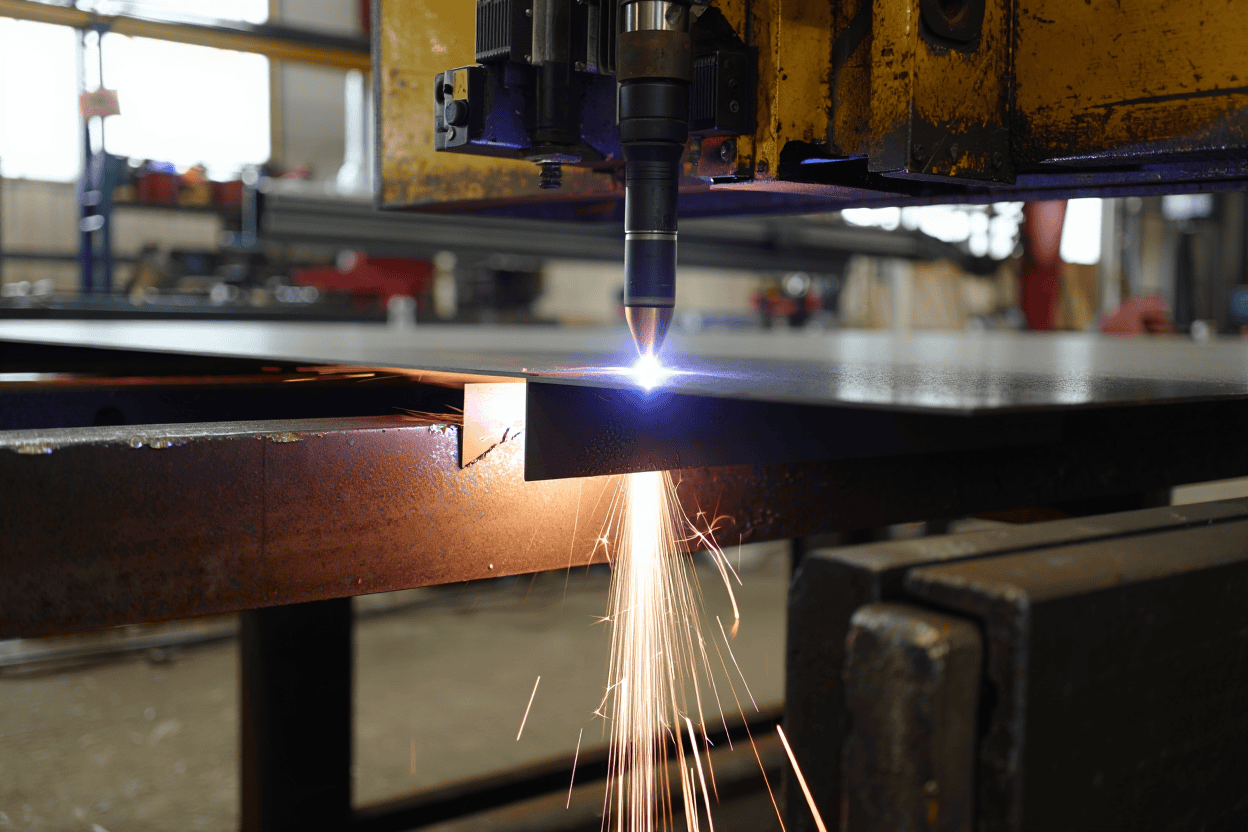
What is Plasma Cutting? A Quick Primer for Metalworkers
Before we categorize various plasma cutting machines, let’s understand the process. In simple terms, a plasma cutter uses compressed air (or other gases) and an electrical arc to create a plasma stream. This plasma is hot enough to melt the metal it touches, while the force of the gas blows the molten material away, creating a cut. It’s faster than oxy-fuel for most mild steel and excels on conductive metals that oxy-fuel struggles with, like stainless steel and aluminum.
10 Types of Plasma Cutters: From Home Shop to Factory Floor
Choosing the right plasma cutting machine starts with knowing what’s available. Here’s your roadmap.
1. Conventional Plasma Cutters (Air Plasma)
Often considered the “original” type, these units use shop air as the primary plasma gas. They are robust, relatively simple, and the most common type found in smaller fabrication shops and for hobbyist plasma cutting.
- Best For: General-purpose cutting of mild steel, stainless, and aluminum up to about 1 inch.
- Ontario Use Case: Perfect for a custom metal shop in Ottawa doing signage, artwork, or general fabrication.
- Keyword Insight: When searching for a reliable plasma cutter for sale in Canada, you’ll often find these.
2. High Definition Plasma Cutters (HD Plasma)
This is where precision meets power. HD plasma cutters use a different torch design and often multiple gases (like oxygen or argon/hydrogen mixes) to create a much more focused, constricted arc. The result? Dramatically cleaner cuts, tighter tolerances, and near-weld-ready edges with minimal dross (slag).
- Best For: Precision fabrication, intricate shapes, and applications where cut quality is critical, often in CNC applications.
- Ontario Use Case: A manufacturing plant in Waterloo producing complex parts for the automotive or aerospace industry.
3. CNC Plasma Cutting Tables
This isn’t just a cutter; it’s a complete automated system. A CNC plasma cutter pairs a plasma power source (often HD) with a computer-controlled gantry that moves the torch. You upload a digital design, and the machine replicates it with speed and flawless consistency.
- Best For: High-volume production, repeat parts, and complex profiles that would be time-prohibitive by hand.
- Ontario Use Case: A steel service centre in the GTA mass-producing parts for the construction industry.
A 2025 report by the Canadian Manufacturing Coalition indicates that over 62% of small and medium-sized manufacturers in Ontario are actively investing in or upgrading digital fabrication tools, including CNC cutting systems, to improve productivity and competitiveness.
4. Portable/Handheld Plasma Cutters
Designed for mobility, these are the workhorses of fieldwork. Modern inverter technology has made them incredibly light and powerful. Many can run on 120V or 240V power, making them versatile for on-site repairs.
- Best For: Contractors, welders, farmers, and scrap metal artists who need to cut in the field, at a job site, or in a tight shop space.
- Ontario Use Case: A pipeline welder in Northern Ontario needing to make quick cuts or bevels on location, or a farmer in Essex County repairing harvester blades.
5. Inverter Plasma Cutters
This refers to the internal technology, not the cut type. Inverter-based plasma cutters are smaller, lighter, more energy-efficient, and offer better arc stability than older transformer-based models. Almost all modern portable and mid-range machines are inverters.
- Best For: Nearly everyone today. They provide more consistent cuts and are easier on your shop’s electrical system.
- Keyword Insight: A plasma cutter with inverter technology is a key feature to look for in your search.
6. Dual Voltage Plasma Cutters
A subtype often combined with portability. These machines can automatically or manually switch between standard 120V (15-20 amp household outlet) and 240V power. On 120V, you get less power for thinner metal; on 240V, you unlock the machine’s full rated capacity.
- Best For: The versatile home shop or mobile welder who needs to work in a garage one day and plug into a dryer outlet or generator the next.
- Ontario Use Case: Ideal for Canadian DIY projects where shop electrical upgrades aren’t feasible.
7. Pilot Arc Plasma Cutters
This feature is now almost standard. A pilot arc is a low-current arc that establishes the plasma path before the torch touches the metal. This allows you to cut painted, rusty, or uneven surfaces and makes pierces more consistent. It also reduces consumable wear.
- Best For: Anyone cutting less-than-perfect metal (e.g., salvage, auto repair, demolition), which is a common reality in many shops.
8. Industrial/Heavy-Duty Plasma Systems
These are the high-amperage beasts designed for continuous, high-volume production cutting. They are built for 8-24 hour daily operation, feature advanced cooling systems, and are paired with high-duty cycles (often 100%).
- Best For: Large-scale manufacturing, shipyards, and major structural steel fabricators.
- Ontario Use Case: A major fabrication yard in Hamilton or Sault Ste. Marie cutting thick plate all day, every day.
9. Specialty & Mechanized Plasma Systems
This category includes systems for very specific applications:
- Pipe Cutting Systems: Orbital cutters that travel around pipe for perfect welds.
- Underwater Plasma Cutting: Reduces noise, glare, and fume emission, ideal for regulated shop environments.
- Multi-Torch CNC Systems: Multiple torches cutting identical parts simultaneously for massive throughput.
10. Air Plasma Cutters with Built-In Air Compressors
An all-in-one solution where the compressor is integrated into the unit. It eliminates the need for a separate, shop-sized air compressor, maximizing portability.
- Best For: Extreme portability where shop air is not available. Trade-off: They are often limited in power and cut capacity compared to units using a dedicated, larger compressor.
- Ontario Use Case: Extremely remote job sites or for a mobile artisan at craft shows.
How to Choose the Right Plasma Cutter: Your 5-Step Decision Matrix
Now, let’s translate this into a choice. Ask yourself these five questions, which align with how most Ontario metal fabricators and hobbyists make their decision.
2025 market analysis by the Fabricators & Manufacturers Association International (FMA) noted a 15% year-over-year increase in North American sales of portable and mid-range plasma cutting systems, signaling a strong shift towards flexible, shop-floor-ready equipment among professionals and serious hobbyists.
1. Assess Your Primary Material & Thickness
This determines your required amperage. A common rule of thumb for handheld plasma cutting is: 1 amp per 0.001 inch of material. So, to cleanly sever 3/8” (0.375”) mild steel, you’d want a minimum of a 40-50 amp machine.
- Pro Tip: Always buy more power than you think you need. A 60-amp machine gives you headroom for 1/2” cuts and better performance on your typical 1/4” work.
2. Consider Your Power Source & Portability Needs
- Garage/Hobbyist (120V): Look for a dual voltage plasma cutter that can start on a 15-20A household circuit for thinner metals.
- Dedicated Shop (240V): For consistent performance on thicker metals, a 240V circuit is non-negotiable. This is the standard for most serious metal fabrication in Canada.
- On-the-Go: Prioritize weight, a sturdy case, and features like dual voltage or a built-in compressor.
3. Evaluate Duty Cycle (The Endurance Stat)
Duty cycle is the number of minutes out of a 10-minute period you can cut at a given amperage before the machine overheats. A 60% duty cycle at 40 amps means you can cut for 6 minutes, then must let the machine cool for 4.
- Hobbyist: 40-50% is often sufficient.
- Professional/Business: Aim for 60% or higher at your most-used amperage. It means less downtime.
4. Match the Machine Type to Your Workflow
Use this quick-reference table:
| Your Primary Work | Recommended Plasma Cutter Type | Key Feature to Look For |
|---|---|---|
| DIY, Auto Repair, Art | Portable, Dual Voltage, Conventional Air | Pilot Arc, Good consumable availability |
| General Fabrication Shop | Mid-Range Inverter (60-80A), HD if budget allows | High Duty Cycle, CNC compatibility for future |
| Precision/Production Work | High Definition (HD) Plasma, often on a CNC table | Cut quality specs (kerf width, angularity) |
| Industrial/Field Work | Industrial Portable or Heavy-Duty System | Rugged build, 100% duty cycle, multi-gas capable |
5. Factor in the True Cost of Ownership
The sticker price is just the start. Consumables, tips, electrodes, swirl rings—are a recurring cost. Research their price and lifespan. Also, consider the cost of a quality air compressor (if needed) and a proper air dryer/filter. Moisture in your air line is the #1 killer of plasma torch consumables, especially in humid Ontario summers.
Final Cut: Making Your Decision as a Canadian Metalworker
Choosing the right plasma cutting machine is about aligning technology with your real-world needs. For most Ontario-based fabricators, farmers, and skilled DIYers, a 60-80 amp inverter plasma cutter with dual voltage capability, a pilot arc, and a solid duty cycle represents the ideal sweet spot of power, versatility, and value.
It’s the tool that can handle the majority of projects that come through a Canadian shop door, from repairing a snowplow frame in January to crafting a custom fire pit for a summer patio.
Ready to Power Your Projects with Precision?
Whether you’re just starting your search for the perfect plasma cutter in Ontario or you’re a seasoned pro looking to upgrade your metal cutting capabilities, getting expert, local advice makes all the difference.
Have a specific project that need plasma cutting, Call (416)-825-2956, or contact us today. Subscribe to our blog for more expert guides, shop tips, and exclusive offers for the Canadian metalworking community
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can I use a plasma cutter in my home garage in Ontario?
A: Absolutely. A 120V/240V dual voltage unit is ideal. Ensure your electrical circuit can handle the amperage draw (check your breaker panel). Always use proper ventilation, plasma cutting produces fumes and particulates.
Q: What’s more important, amperage or duty cycle?
A: They work together. Amperage determines what you can cut. Duty cycle determines how long you can cut it continuously. For professional use, a higher duty cycle is often more valuable than a slight amperage boost.
Q: I see cheap plasma cutters online. What’s the catch?
A: Often, the cut quality, durability, and duty cycle are poor. Consumables may be proprietary, expensive, or hard to find in Canada. Support and repair can be non-existent. Investing in a reputable brand (like Hypertherm, Lincoln Electric, Miller, or even quality import brands with strong Canadian distributor support) saves money and headache in the long run.
Q: Do I need a special air compressor?
A: Yes. You need a compressor that can deliver adequate CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) at the required PSI (check your cutter’s manual). As mentioned, a quality moisture filter/regulator is not optional; it’s essential for protecting your investment.