14
Oct
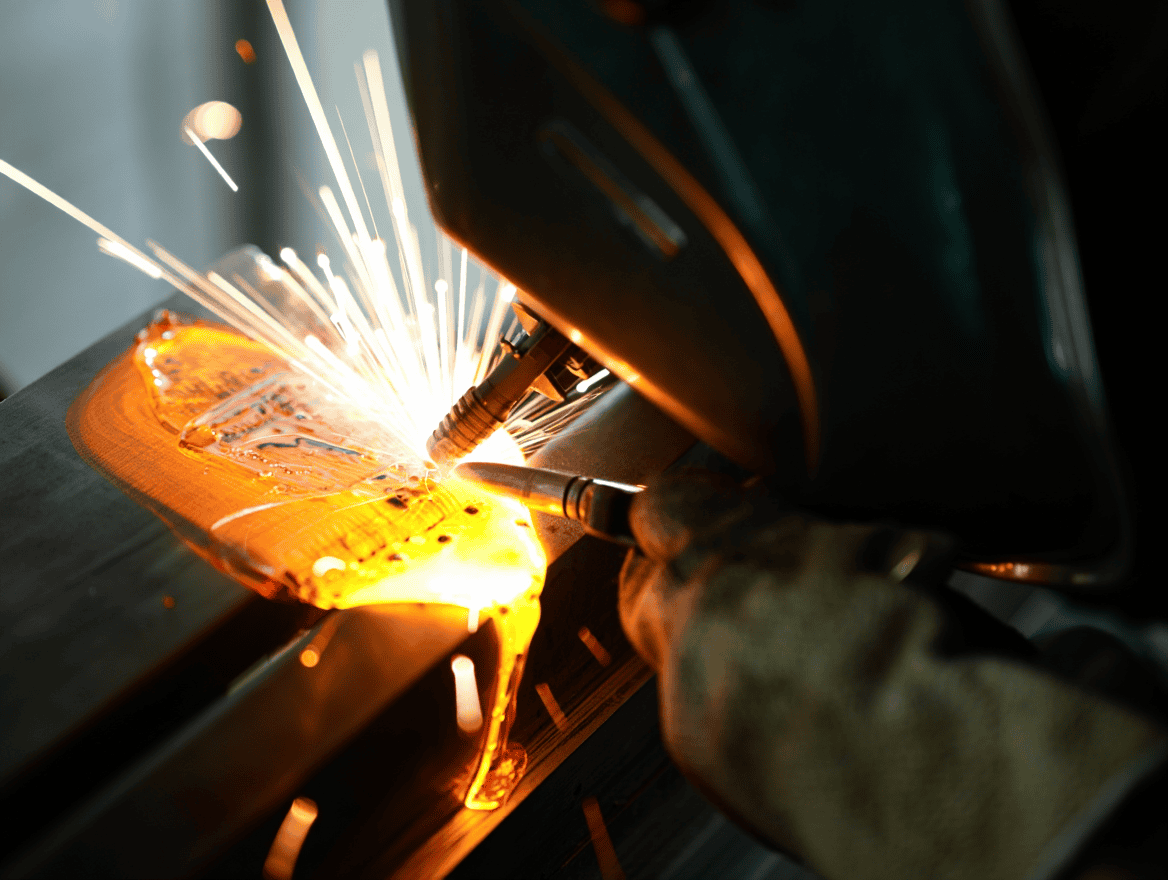
The laser, invented in 1960, transformed the world, including welding and fabrication, which were once entirely manual and labor-intensive processes. Welding is essential across industries that rely on the strength of metals, from construction to equipment manufacturing. The advent of laser welding revolutionized fields like aerospace and medical instrumentation, where finer, stronger welds are critical. For those unfamiliar with the process, you may wonder what laser welding is and how it works. Below, we explore the types of laser welding to provide insight.
Understanding Different Types of Laser Welding
-
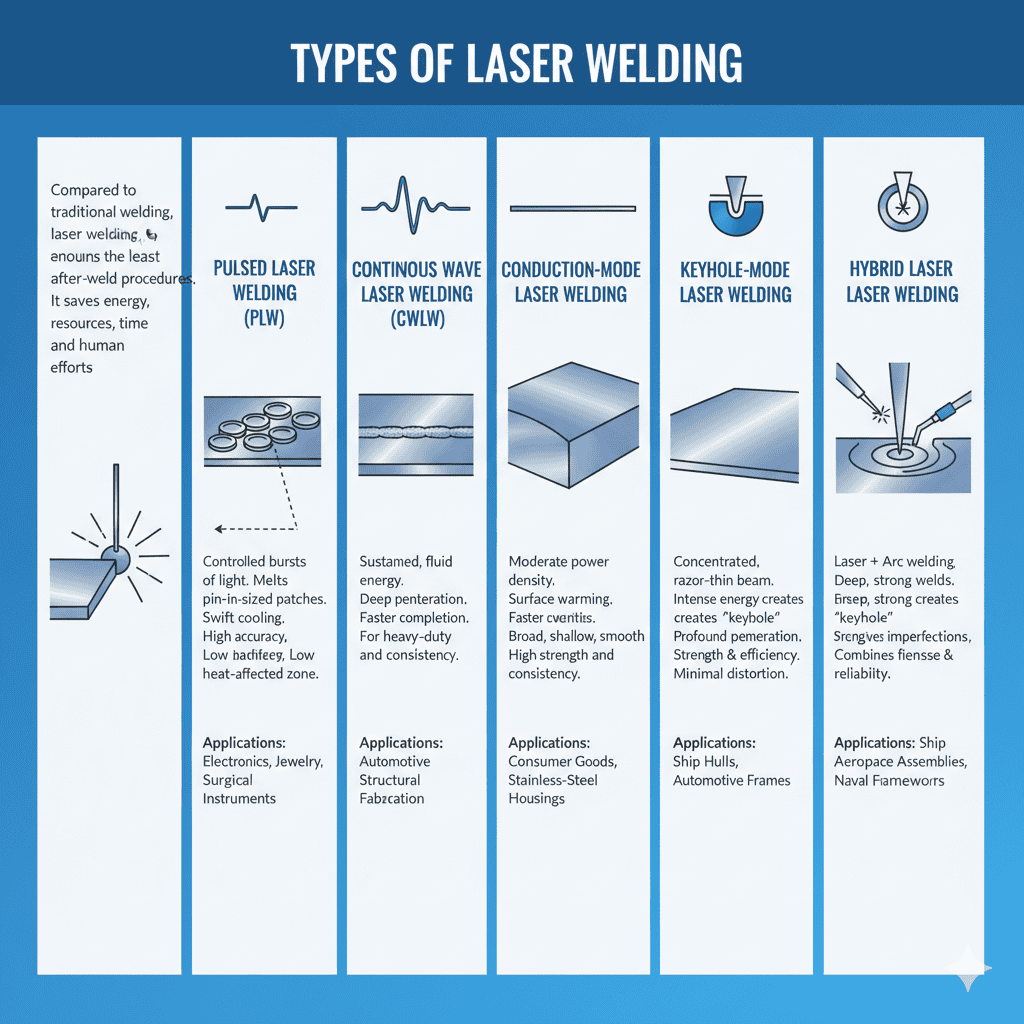
Pulsed Laser Welding (PLW)
Imagine a laser pulsing with rhythmic bursts of energy, like a mechanical heartbeat. That’s pulsed laser welding. Using advanced laser welding machines, it delivers controlled bursts of light, each melting a pin-sized patch of metal before cooling swiftly and striking again. The result is a series of overlapping weld spots—tiny, robust, and precisely aligned.
This method is ideal for thinner materials requiring meticulous welds, as it minimizes distortion and warping. Its accuracy makes it perfect for electronics, jewelry, and surgical instruments, limiting the heat-affected zone (HAZ) to protect surrounding materials from thermal damage.
-
Continuous Wave Laser Welding (CWLW)
If pulsed welding is a heartbeat, continuous wave laser welding is a steady, flowing stream. It projects a continuous beam of concentrated energy, melting and fusing metal as it glides along a joint. This uninterrupted power enables deep penetration and faster weld completion, ensuring unyielding strength.
This method excels with heavy-duty, thicker materials. Automotive bodywork, structural fabrication, and mechanical enclosures benefit from its long, consistent, and deeply bonded welds. It’s ideal for production lines demanding relentless durability.
-
Conduction-Mode Laser Welding
Unlike methods that penetrate deeply, conduction-mode welding works elegantly on the surface. It uses moderate power density to warm the metal’s surface, allowing heat to flow inward naturally. The result is a broad, shallow, and impeccably smooth weld, crafted for both aesthetics and strength.
This technique shines in applications where appearance matters as much as function, such as polished consumer goods, stainless steel housings, and precision casings. The welds are sleek, often requiring no polishing or post-treatment, making conduction-mode welding the cosmetic surgeon of the welding industry.
-
Keyhole-Mode Laser Welding
Keyhole-mode laser welding is precision fused with intensity. A concentrated beam channels immense energy into a tiny focal point, creating a “keyhole” cavity in the metal. Within this void, the laser’s energy penetrates deeply, forming a seamless, narrow weld that balances strength and efficiency.
Unlike traditional welding methods, which struggle to combine durability and accuracy, keyhole-mode welding excels in both. It’s critical for high-stakes applications like aerospace assemblies and naval frameworks, delivering clean welds with minimal splatter and near-zero distortion, brute power with a craftsman’s finesse.
-
Hybrid Laser Welding
Hybrid laser welding is a marvel of engineering synergy, blending the pinpoint precision of laser welding with the resilience of arc welding. The laser cuts deep into the metal while the arc supplements it with filler material and structural reinforcement, working in harmony over the same molten pool.
The result is extraordinary: deep, strong welds that tolerate imperfections. From sprawling ship hulls to high-speed automotive frames, hybrid laser welding delivers strength and speed with unmatched balance, marrying the finesse of lasers with the reliability of traditional arc techniques.
Benefits of Laser Welding
Compared to traditional welding, laser welding requires minimal post-weld processing. Grinding, polishing, or cleaning is often unnecessary, as laser welds avoid warping and imperfections. This saves energy, resources, time, and labor.
FAQs
What is the main advantage of laser welding over traditional arc welding?
Laser welding offers superior accuracy, reduced heat input, and higher-quality welds compared to traditional arc welding.
What is the most noticeable difference between a traditional weld and a laser weld?
Laser welds are cleaner, with a smaller heat-affected zone (HAZ), minimal material distortion, shrinkage, or stress compared to traditional welds.
When is pulsed laser welding most effective?
It’s ideal for thin materials requiring precision and a delicate approach, ensuring perfection without distortion.
Does laser welding require filler material?
Often, no—especially in autogenous (self-fusing) keyhole or conduction welding of well-fitted joints.